In the field of fiber optic communication, SFP optical transceiver are key components for transmitting and receiving optical signals. In the SFP optical transceiver market, single-mode (SM) and multi-mode (MM) are two common types, which differ significantly in their application, performance characteristics, and technical parameters.
Definition and Background
SFP optical transceiver is a device that integrates optoelectronic components, optical components, and electronic components to transmit and receive high-speed optical signals through optical fibers. Based on the type of fiber optic transceiver, SFP optical transceiver can be divided into single-mode SFP optical transceiver and multi-mode SFP optical transceiver. Single-mode fiber optic transceivers allow only one beam of light to propagate through them, while multi-mode fiber optic transceivers allow multiple beams of light to propagate through them.
Main Differences:
Different Wavelengths
Single-mode SFP optical transceivers typically operate at wavelengths of 1310nm or 1550nm, which have low transmission loss in optical fibers and are suitable for long-distance transmission. Multimode SFP optical transceivers, on the other hand, typically operate at wavelengths of 850nm or 1300nm, which have relatively higher transmission loss in optical fibers and are suitable for short-distance transmission.
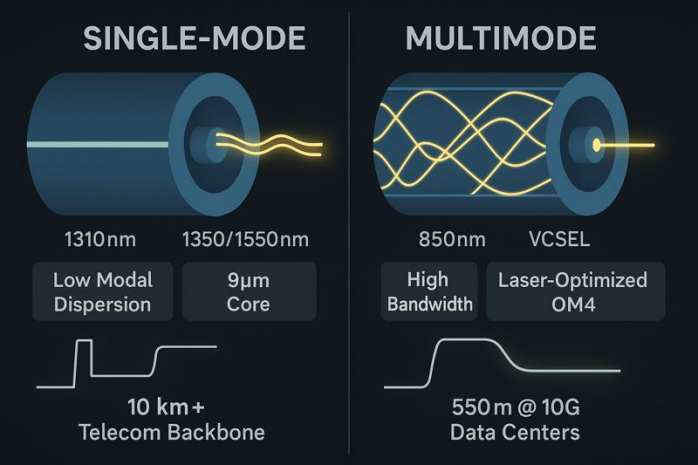
Different Transmission Distances
Single-mode optical SFP transceivers are commonly used for long-distance transmission, with transmission distances reaching 150 to 200 km, or even further. Due to the smaller core diameter of single-mode fiber, signal propagation loss is reduced, enabling longer transmission distances. Multimode SFP optical transceivers, on the other hand, are mostly used for short-distance transmission, typically less than 2 km. Multimode fiber has a larger core diameter, allowing multiple light beams to enter, but this leads to signal dispersion and attenuation over long distances.
Different Applications
Single-mode SFP optical transceiver are primarily used in lines with relatively high transmission rates and long distances, such as metropolitan area networks, wide area networks, connections within and between data centers, backhaul transmission for wireless communication base stations, and long-distance fiber optic communication systems. These application scenarios have high requirements for signal transmission distance and bandwidth. Multimode SFP optical transceivers, on the other hand, are mostly used in short-distance transmissions, such as access layer and aggregation layer networks, data communication, storage area networks (SANs), and local area networks. These application scenarios prioritize high-density, high-bandwidth transmission performance.
Different Light Sources
The light source for single-mode SFP optical transceiver is either an LD (laser diode) or an LED with a narrow spectral linewidth, which provides a stable single-mode output. The light source for multi-mode optical SFP transceiver, on the other hand, is typically a light-emitting diode or a laser, which generates multi-mode optical signals.
Different Prices
Although single-mode fiber is cheaper than multi-mode fiber, single-mode SFP optical transceivers are more expensive than multi-mode SFP optical transceivers. This is because single-mode SFP optical transceivers require higher precision and more complex manufacturing processes, and also offer superior performance.
Precautions for Use
When using single-mode SFP optical transceivers, ensure that the actual received optical power is less than the overload optical power to avoid damaging the equipment. The optical power can be measured using a power meter, and an optical attenuator can be used to adjust the power level.
When using single-mode SFP optical transceivers, there should be sufficient margin in the received power to ensure signal stability and reliability.
Multimode SFP optical transceivers can only transmit signals of a single wavelength and cannot be used with multiplexers.
Multimode SFP optical transceivers are designed to operate only on multimode optical fibers and cannot be used with single-mode optical fibers.
Conclusion
In summary, single-mode and multi-mode SFP optical transceiver differ significantly in terms of wavelength, transmission distance, fiber type, light source, application range, and price. When choosing which type of SFP optical transceiver to use, a comprehensive consideration of the specific application scenario and requirements is necessary. Furthermore, it is important to pay attention to relevant usage precautions when using SFP optical transceivers to ensure the normal operation of the equipment and stable signal transmission.



