In the complex world of fiber optic networking, ensuring the compatibility of SFP module (Small Form factor Pluggable) is crucial for the smooth operation and optimal performance of your network. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to check SFP module compatibility.
Understand the Basics of SFP Transceiver Module
SFP module is hot pluggable optical transceiver that come in various types, such as singlemode and multimode, with different data rates and wavelengths. They are used to connect network equipment like switches, routers, and network interface cards (NICs) via fiber optic cables. Compatibility issues can arise due to differences in these characteristics.
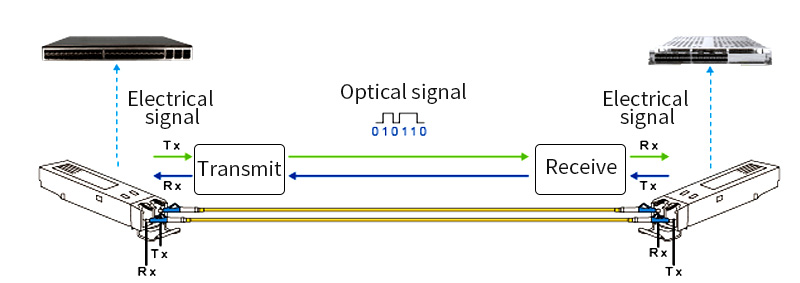
Check the Network Equipment Manufacturer’s Specifications
Model Compatibility
The first step is to refer to the documentation or website of the network equipment (e.g., switch or router) manufacturer. They usually provide a list of compatible SFP module. For example, Cisco routers have specific SFP module that are approved for use with their equipment. Check if the SFP fiber module you intend to use is on that list.
Some manufacturers also offer compatibility matrices that detail which SFP module work with different firmware versions of their equipment. Make sure you have the correct firmware installed and that the SFP transceiver module is compatible with it.
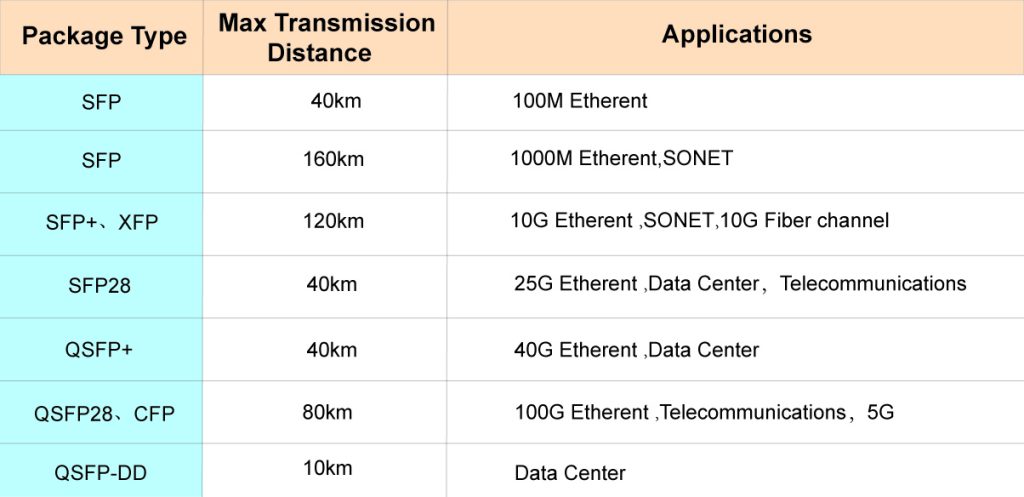
Transceiver Type and Data Rate
Ensure that the type of SFP module (singlemode or multimode) matches the requirements of the network equipment. If the equipment is designed for singlemode fiber connections, using a multimode SFP module may result in poor performance or no connection at all.
The data rate of the SFP module should also be supported by the network device. For instance, if a switch port only supports up to 1Gbps data rate, a 10Gbps SFP module will not work properly.
Consider the Fiber Optic Cable Compatibility
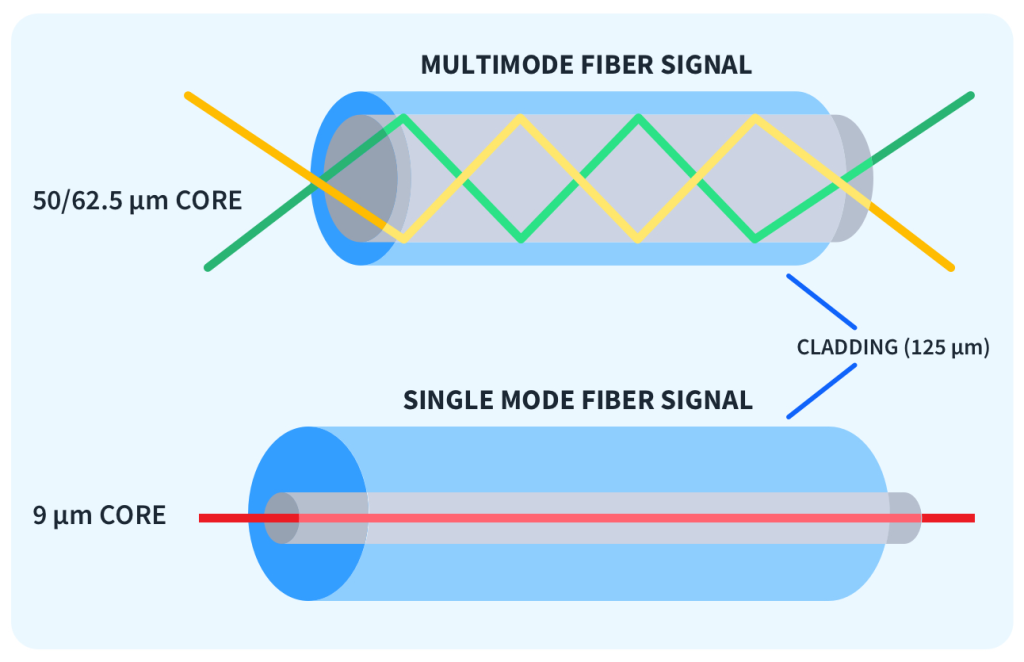
Fiber Mode
As mentioned earlier, singlemode SFP module require singlemode fiber optic cables, while multimode SFP module need multimode cables. Check the fiber cable type and ensure it aligns with the SFP module. Using the wrong fiber cable can lead to signal attenuation and connection failures.
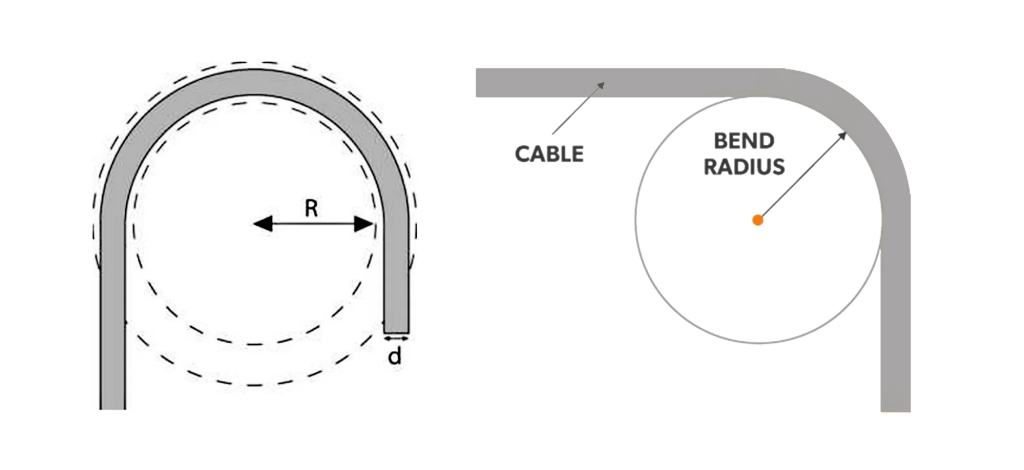
Patch Cord Length and Bend Radius
The length of the fiber optic patch cord can affect the performance of the SFP module. Some SFP module has limitations on the maximum cable length they can support. For example, a particular 1Gbps multimode SFP module may only work effectively with cable lengths up to 550 meters.
Also, consider the bend radius of the fiber patch cord. Exceeding the recommended bend radius can cause damage to the fiber and impact the signal quality. Ensure that the cable installation adheres to the proper bend radius requirements for both the cable and the SFP module.
Look at the Wavelength and Optical Power Specifications
Wavelength
SFP transceiver module operate at specific wavelengths. Common wavelengths for singlemode SFP module are 1310nm and 1550nm, while multimode SFP modules may operate at 850nm or 1310nm. The network equipment and the SFP transceiver module must have compatible wavelength settings. If the wavelengths don’t match, the optical signal may not be properly transmitted or received.
Optical Power
Check the optical power requirements and capabilities of the SFP module and the network equipment. The transmit power of the SFP module should be within the acceptable range of the receiving equipment, and vice versa. If the optical power is too low, the signal may be too weak to be detected, and if it’s too high, it can damage the receiver.
Test and Verify Compatibility
Initial Plug-in and Link Status
Once you believe the SFP module is compatible based on the above checks, carefully plug it into the network equipment. Check the equipment’s interface or management console to see if the link is established. If the link light is off or shows an error, it indicates a possible compatibility issue.

Performance Testing
After a successful link establishment, conduct performance tests. Use network monitoring tools to check the data transfer rate, packet loss, and latency. If the performance is below expectations or there are errors, it could be due to a compatibility problem that was not initially detected. For example, a slow data transfer rate could indicate an issue with the SFP module’s data rate compatibility or a problem with the fiber cable quality.
Conclusion
Checking SFP transceiver compatibility requires a careful examination of multiple factors, including network equipment specifications, fiber optic cable characteristics, wavelength and optical power settings, and thorough testing. By following these steps, you can ensure that your SFP fiber module work seamlessly with your network infrastructure, maximizing the performance and reliability of your fiber optic network.



