MPO fiber patch cord plays a crucial role in modern high-speed data transmission networks. However, like any other technology, they are prone to certain failure modes. Understanding these common issues can help network engineers and technicians take proactive measures to prevent or address them promptly.
Fiber Misalignment
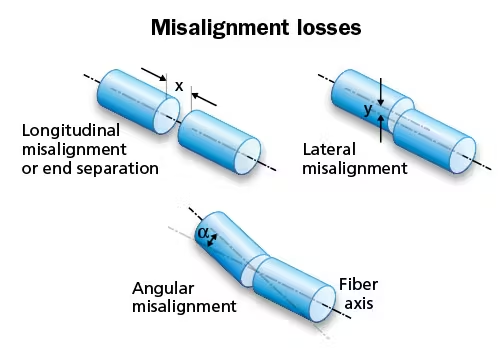
One of the most prevalent failure modes is fiber misalignment, which will occur during the manufacturing process if the fibers within the MPO connector are not precisely positioned. Even a slight misalignment can lead to significant signal loss and degradation. Over time, environmental factors such as temperature changes, vibrations, or physical stress on the MPO-MPO fiber cable can also cause the fibers to shift out of alignment. In a data center where multiple MPO connections are used, a single misaligned fiber in an MPO patch cord can disrupt the entire network link, resulting in slow data transfer or even complete connection failures.
Connector Damage
The connectors of MPO optical patchcord are subject to wear and tear. Repeated plugging and unplugging can cause scratches, dents, or deformation on the MPO connector surfaces. These physical damages can affect the optical performance of the connector. For example, a scratched connector may introduce additional insertion loss as the light signal is scattered or absorbed irregularly. Moreover, if the connector is not properly protected, it can be exposed to dust, dirt, or other contaminants. These particles can settle on the fiber end-faces and obstruct the light path, leading to signal attenuation or even complete signal blockage.

Cable Bending Beyond Tolerance
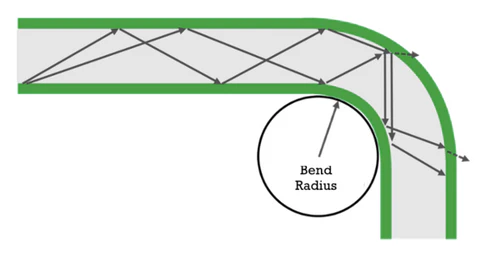
MPO cable has a specified minimum bend radius. If the MPO fiber cable is bent too sharply, beyond this tolerance, it can cause microbending or macrobending of the fibers inside. Microbending occurs when the fiber is subjected to small-scale deformations, usually due to pressure points along the cable. Macrobending is more significant and visible bending of the cable. Both types of bending can cause light to leak out of the fiber, increasing insertion loss and reducing the overall signal strength. In a crowded cable tray or when cables are routed through tight spaces, it is easy to accidentally exceed the bend radius, especially if proper cable management practices are not followed.
Moisture Ingress
If the MPO fiber jumper’s outer jacket is damaged or has poor sealing, moisture can seep into the MPO cable. Water molecules can cause several problems. They can corrode the metal components within the MPO cable, such as the fiber coating or the connector pins. Corrosion can lead to increased resistance and signal degradation. Additionally, moisture can also affect the refractive index of the fiber, causing light scattering and absorption. In humid or wet environments, such as underground cable installations or in areas with high humidity levels, moisture ingress is a significant concern and can lead to premature failure of the MPO fiber cable.
Temperature Fluctuations
Extreme temperature changes can have a negative impact on MPO jumper. High temperatures can cause the expansion of the MPO cable materials, potentially putting stress on the fibers and connectors. This stress can lead to fiber misalignment or connector loosening. On the other hand, low temperatures can make the cable more brittle, increasing the risk of cracking or breaking. In outdoor installations or in environments where temperature control is not optimal, such as in industrial settings with heat-generating equipment or in unconditioned server rooms, temperature fluctuations can be a major factor contributing to MPO fiber patch cord failures.
Cable Tension and Crush
During installation or maintenance, excessive tension or compression of MPO optical cables can damage their internal fiber structure. Excessive tension can cause the fibers to stretch or break, while compression can deform the cable and interfere with optical transmission. This is especially important to consider when MPO|MTP cables are being routed through conduits or when they are bundled together with other cables. Improper cable handling and installation techniques can easily result in cable tension and crush issues.
Conclusion
MPO fiber patch cord can experience various failure modes, ranging from fiber misalignment and connector damage to issues related to cable handling and environmental factors. By being aware of these common problems and implementing proper cable installation, maintenance, and protection strategies, network operators can enhance the reliability and lifespan of their MPO fiber cable installations and ensure the smooth operation of their high speed data networks. Regular inspections and testing of MPO jumper an also help in early detection and remediation of potential failures.



