In the complex world of modern telecommunications and data networking, the transceiver module stands as a crucial and highly sophisticated component. But what exactly is optic transceiver? Let’s delve deeper.
What are the Basic Function of an Transceiver?
An optic transceiver, also known as an transceiver module, is a device that serves as the bridge between electrical and optical signals. Its primary function is to convert electrical data signals from network equipment such as switches, routers, and servers into optical signals for transmission over fiber optic cables and vice versa. In short, it enables seamless communication between electrical devices and the optical network infrastructure.
What are the Components of an Transceiver?
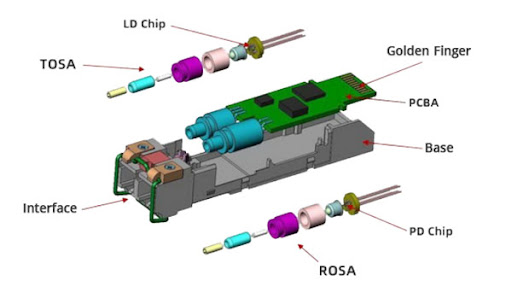
The fiber optic transceiver consists of two main parts: the transmitter and the receiver.
Transmitter: This component uses a light source, usually a laser diode or a light-emitting diode (LED), to convert electrical data into optical signals. These optical signals are then sent through the fiber optic cable to their destination.
Receiver: The receiver contains a photo detector that detects the incoming optical signals and converts them back into electrical signals that can be processed by the connected equipment.
Together, these components ensure the efficient transfer of data for the transceiver.
Form Factors and Specifications
Optic transceiver comes in a variety of form factors and specifications to meet different networking needs.
Common Form Factors: Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP), SFP+, QSFP+ (Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable), QSFP28, QSFP-DD, OSFP, CFP are some of the common form factors. Each offers different levels of port density, power consumption, and data transfer rates.
Data Transfer Rates: Transceiver module can support a wide range of data transfer rates, from a few megabits per second to hundreds of gigabits per second. The choice of transceiver depends on the specific requirements of the network.
Reach or Distance: Some optic transceiver are designed for short distance transmissions within a data center, while others can support long haul transmissions over thousands of kilometers.
The availability of different form factors and specifications allows network administrators to choose the most suitable transceiver for their particular application.
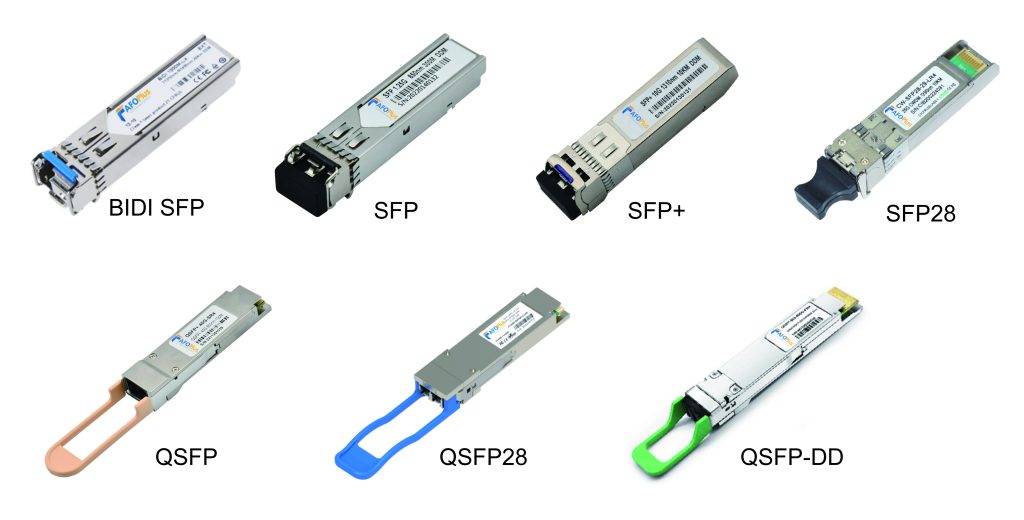

Division of transceivers by Connectors
Optic transceiver use different types of connectors to make connections to fiber optic cables. Here are some of the common connector types used in optic transceiver: LC connector/SC connector/RJ45 connector/MTP/MPO connector.

Division of Transceivers due to Distance
Short Range Transceivers
Short-range optic transceiver are designed for efficient communication over relatively short distances, such as rooms in a single building or data centers. They are ideal for fast data exchange within a single location, providing efficient connectivity between devices in the same space.
Long Range Transceivers
Long range optic transceiver are designed to cover longer distances, such as connections between different buildings or even cities. Their advanced features allow them to connect separate locations, enabling continuous data exchange over long distances, which is especially important in urban or regional environments.
Extra-Long Range Transceivers
Ultra long range optic transceiver are designed for extended distance data transmission even through transcontinental or transoceanic communications. An example of an application is undersea cable, where data are traveling oceans.
Importance in Networking
The importance of optic transceivers in modern networking cannot be overstated.
High-Speed and Reliable Transmission: Fiber optic cables offer significantly higher bandwidth and lower signal attenuation compared to traditional copper cables. Optic transceivers enable the full potential of fiber optic technology, providing high-speed, low-latency, and reliable data transmission.
Hot-Swappable Design: Most optic transceivers are hot swappable, meaning they can be easily inserted and removed from network equipment without powering down the system. This simplifies network maintenance and upgrades, reducing downtime and increasing overall network efficiency.

Conclusion
Optic transceiver is essential components in today’s digital age, playing a vital role in enabling efficient and high-speed data communication across various networks. The technological aspects surrounding optical transceivers can be difficult to understand especially if you are not technologically inclined. However, optical transceivers are crucial if you have a network that needs to transfer and receive heavy digital traffic over long distances speedily.
If you are wondering what type of optical transceiver your company could benefit from using, you should consider finding out more from AOFPLUS. We are well versed in all things associated with optical transceivers and can help you understand what more you need to know.



